Key Takeaways
- Automation replaces manual work with connected systems that move, track, and manage goods in real time.
- RFID and AI tools boost accuracy, visibility, and speed across warehousing and distribution.
- Standardized materials and data flows make automation more reliable and easier to scale.
- RFID-enabled plastic pallets create a durable, traceable base for automated handling systems.
- Pallet pooling networks clean, inspect, and reuse plastic pallets—cutting waste and improving supply chain sustainability.
What Is Supply Chain Automation?
Supply chain automation uses machines, sensors, and software to move, track, and manage goods with less manual effort. It replaces repetitive work with connected systems that record and share data in real time.
Automation connects suppliers, warehouses, and distributors through one digital network. Robots handle material movement, RFID scanners record shipments automatically, and software platforms forecast demand while balancing inventory. The result is faster, more accurate operations with fewer disruptions.
Manual tracking often leads to missed scans, lost products, and incomplete records. Automation removes these gaps by creating consistent, traceable visibility from production to delivery. It builds cleaner data, safer workplaces, and steadier performance.
Modern automation extends beyond robotics. Shared data, predictive analytics, and machine-to-machine communication now form the backbone of efficient, connected supply chains.
What Are Examples of Supply Chain Automation?
Automation touches nearly every stage of logistics:
- Material handling: Robots, conveyors, and automated guided vehicles (AGVs) move goods safely and consistently.
- Tracking systems: RFID tags and barcode scanners update shipment data instantly.
- Intelligent software: AI platforms forecast demand, plan routes, and optimize inventory.
In advanced operations, RFID-enabled pallets communicate with AGVs, telling machines what they’re carrying and where to go. This removes manual scanning, improves speed, and creates live visibility across every shipment.
A practical example is a warehouse using RFID-enabled plastic pallets. Each pallet transmits location and condition data in real time, removing the need for manual scans. This visibility keeps inventory accurate, prevents loss, and supports traceability.
Getting the Most out of Supply Chain Automation
To get the best results, connect your systems, standardize workflows, and use traceable materials.
- Connect systems: Link warehouse, transport, and inventory platforms to share data in real time. This improves coordination and reduces delays.
- Improve visibility: Add RFID tags, barcodes, and sensors to track pallets, products, and equipment automatically.
- Keep workflows consistent: Standardize labeling, pallet handling, and inspection steps so automation runs smoothly.
- Use durable, traceable assets: RFID-enabled plastic pallets from iGPS provide a consistent, automation-ready base for shipments. They’re reliable and won’t splinter or jam equipment like wood pallets.
- Integrate AI: Predictive analytics helps forecast demand, schedule maintenance, and identify bottlenecks before they happen.
- Measure and refine: Automation isn’t static. Review performance data to adjust processes, strengthen reliability, and plan for growth.
- Plan for Scalability: Design your automation strategy to grow with you. Modular equipment, cloud-based software, and standardized pallets make it easier to scale operations without major reconfiguration
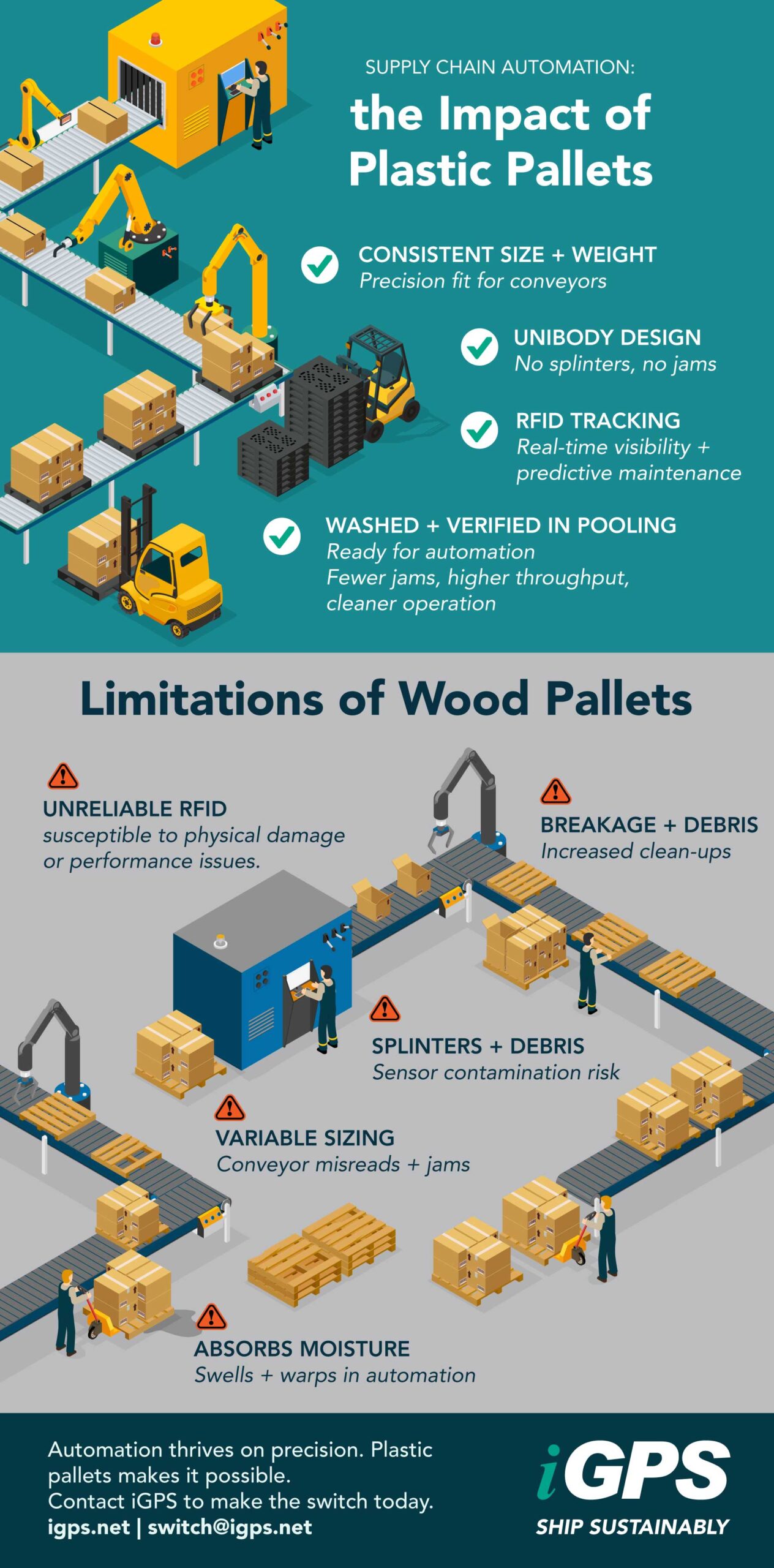
The Importance of Using Plastic Pallets
Plastic pallets play a central role in making automation work effectively. Automated systems rely on precision—consistent dimensions, reliable weight, and clean surfaces—to keep conveyors, sensors, and robotic arms operating smoothly. Wood pallets often fail in this environment; they vary in size, absorb moisture, and can splinter or warp, which leads to jams, downtime, and costly maintenance.
Plastic pallets, by contrast, maintain exact tolerances across every unit. Their unibody construction provides stability under heavy loads and ensures seamless compatibility with automated guided vehicles, robotic picking systems, and high-speed sortation equipment. Each pallet moves predictably through conveyors and automated storage systems, reducing error rates and protecting equipment.
RFID-enabled plastic pallets take automation even further. Each pallet carries a unique digital identity that allows scanners and software systems to track its location, status, and load in real time. This visibility supports automated inventory control, route optimization, and predictive maintenance, turning physical assets into active data points within the supply chain. As detailed in Inbound Logistics’ Smart Stack: Pallets Load Up Innovation, the latest pallet designs are lighter, stronger, and optimized for robotic handling—ensuring smooth integration with automated systems and improving both productivity and safety.
When integrated into a pallet pooling network, the advantages multiply. Every pallet is inspected, washed, and verified before reuse, keeping circulation consistent and automation-ready. Together, these features make plastic pallets a critical component for maintaining speed, accuracy, and reliability in modern supply chain automation.
Building a Self-Optimizing Supply Chain Automation
Automation is moving toward intelligence. Smart pallets, AI-driven forecasting, and connected systems are creating supply chains that adapt automatically—rerouting shipments, predicting maintenance, and preventing downtime before it occurs.
This type of self-optimizing supply chain is already emerging, as highlighted in The Tech-Enhanced Future of Pallet Pooling, where AI and automated inspection tools are redefining how assets circulate and communicate across networks.
These self-optimizing systems rely on continuous data feedback. Assets communicate, software responds in real time, and teams focus on strategy rather than manual tracking. The result is a supply chain that runs cleaner, faster, and smarter.
Conclusion
Supply chain automation succeeds when technology, people, and materials work in sync. From RFID tracking to AI forecasting and plastic pallet pooling, every connected system builds cleaner data, safer operations, and smarter logistics.
Automation isn’t just faster—it’s more reliable. Companies adopting these systems today are shaping the future of intelligent, sustainable supply chains.
FAQ
Which supply chain tasks to automate first for biggest impact
Start with the tasks that slow teams down or cause the most errors:
- Inventory tracking with RFID or barcodes for instant visibility.
- Material handling using conveyors, robotic palletizers, and AGVs.
- Data reporting that consolidates scanner and sensor information.
These improvements create consistency and free teams for higher-value work.
Best automation tools for warehouse and inventory management
The best automation tools for warehouse and inventory management improve accuracy, speed, and visibility across daily operations. These technologies connect physical movement with real-time data to keep supply chains efficient and predictable.
Key tools include:
- Warehouse Management Systems (WMS) for tracking and order accuracy.
- RFID and barcode systems for automated inventory updates.
- Robots and conveyors for safe, efficient movement.
- Cloud logistics platforms to link suppliers, carriers, and warehouses.
Combined, they reduce waste, errors, and delays.
Together, these tools reduce errors, increase efficiency, and create a connected system that supports complete supply chain automation.
How to manage workforce change and retrain staff for automation
Managing workforce change during supply chain automation starts with clear communication and continuous training. The goal isn’t to replace workers, but rather shift their focus from manual tasks to higher-value work that supports automated systems.
Steps to manage and retrain effectively:
- Communicate early and clearly: Explain why automation is being adopted and how it improves safety, speed, and accuracy. Transparency reduces resistance and builds trust.
- Provide focused training: Offer hands-on instruction for operating and maintaining automated tools like robots, RFID systems, and warehouse software.
- Create hybrid roles: Combine technical skills with human oversight—such as technicians managing robotic palletizers or monitoring RFID-enabled plastic pallets.
- Recognize adaptability: Reward employees who embrace new skills or lead automation efforts. Acknowledge progress to build morale and retention.
Supporting workers through change strengthens engagement, ensures smoother adoption, and creates a more capable, future-ready supply chain team.
How should a company prepare for automation?
Assess current workflows, identify manual bottlenecks, and standardize materials like pallets. Clean, connected data systems ensure a smoother rollout.
What’s the ROI timeline for automation?
Most companies see measurable returns within 12–24 months from reduced labor, fewer breakdowns, and faster throughput. Durable plastic pallets extend those savings by lowering maintenance and replacement costs.
What are the biggest challenges in automating logistics?
Data inconsistency, poor system integration, and mismatched equipment. Solving these through standardization and training delivers higher ROI and long-term stability.
How does automation support sustainability goals?
Automation improves efficiency, reducing emissions and waste. Lightweight, recyclable plastic pallets use less fuel and keep materials in circulation—aligning performance with sustainability.
Automation and AI are reshaping how goods move through the supply chain and iGPS is helping lead that shift. Our RFID-enabled plastic pallets provide the precision, consistency, and data connectivity that automation depends on. Built for robotic handling and real-time visibility, they keep operations cleaner, faster, and more reliable. To learn how iGPS can support your automation and efficiency goals, call 1-800-884-0225, email switch@igps.net, or visit our contact page.




